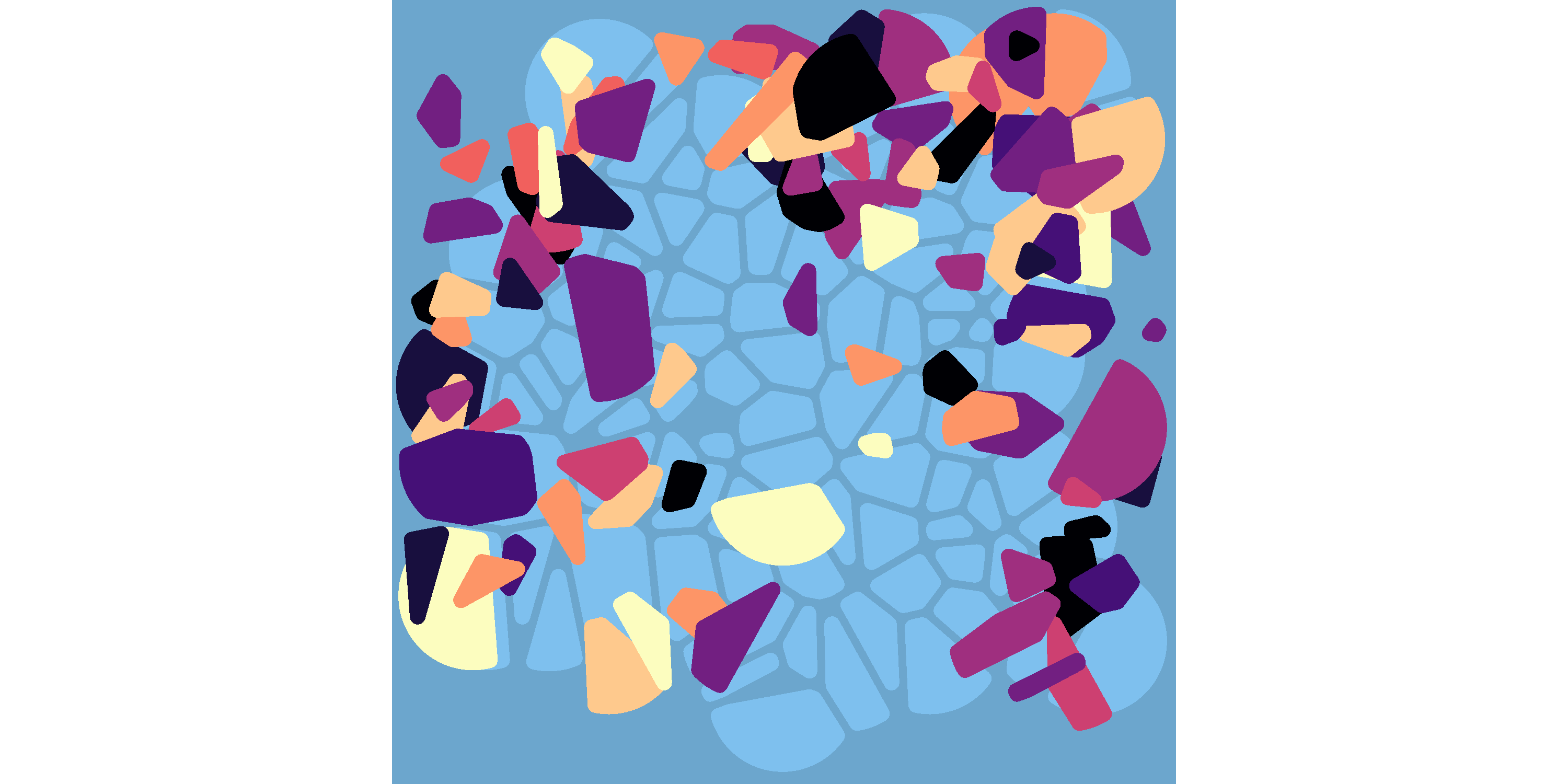The goal of voronoise is to make pretty pictures. It is a very minor tweak on the voronoi tesselations provided by the ggforce package. You can install the development version of voronoise from GitHub with:
remotes::install_github("djnavarro/voronoise")
Example
Create a tibble with columns specifying the x and y coordinates, and the colours to be associated with the corresponding Voronoi cell
library(voronoise) #> Loading required package: ggplot2 #> Loading required package: ggforce set.seed(1) dat <- tibble::tibble( x = runif(n = 50, min = .1, max = .9), y = runif(n = 50, min = .1, max = .9), shade = sample(colours(), size = 50, replace = TRUE) ) dat #> # A tibble: 50 x 3 #> x y shade #> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> #> 1 0.312 0.482 tan #> 2 0.398 0.789 grey43 #> 3 0.558 0.450 plum4 #> 4 0.827 0.296 rosybrown #> 5 0.261 0.157 grey26 #> 6 0.819 0.180 springgreen4 #> 7 0.856 0.353 gold3 #> 8 0.629 0.515 grey68 #> 9 0.603 0.630 navajowhite2 #> 10 0.149 0.425 tomato #> # … with 40 more rows
The voronoise_base() function initialises a ggplot object
voronoise_base(dat)

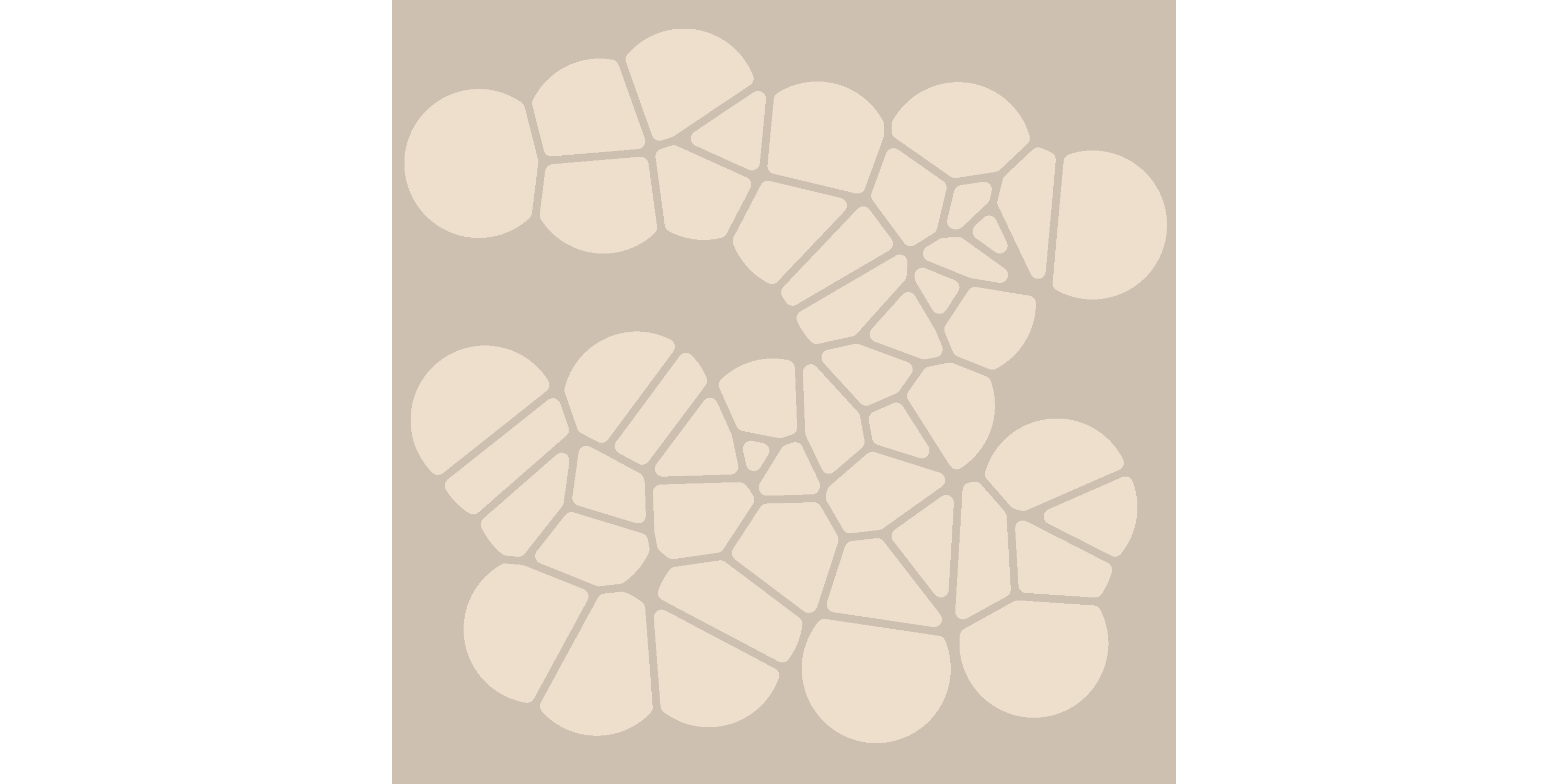
The default behaviour of geom_voronoise() is identical to ggforce::geom_voronoi_tile() with some parameter values changed. It does not perturb the location of any of the tiles:
voronoise_base(dat) + geom_voronoise(fill = "antiquewhite2")
To perturb the tiles we need to pass it a perturb function:
voronoise_base(dat) + geom_voronoise(fill = "antiquewhite2") + geom_voronoise(perturb = perturb_uniform(.2))
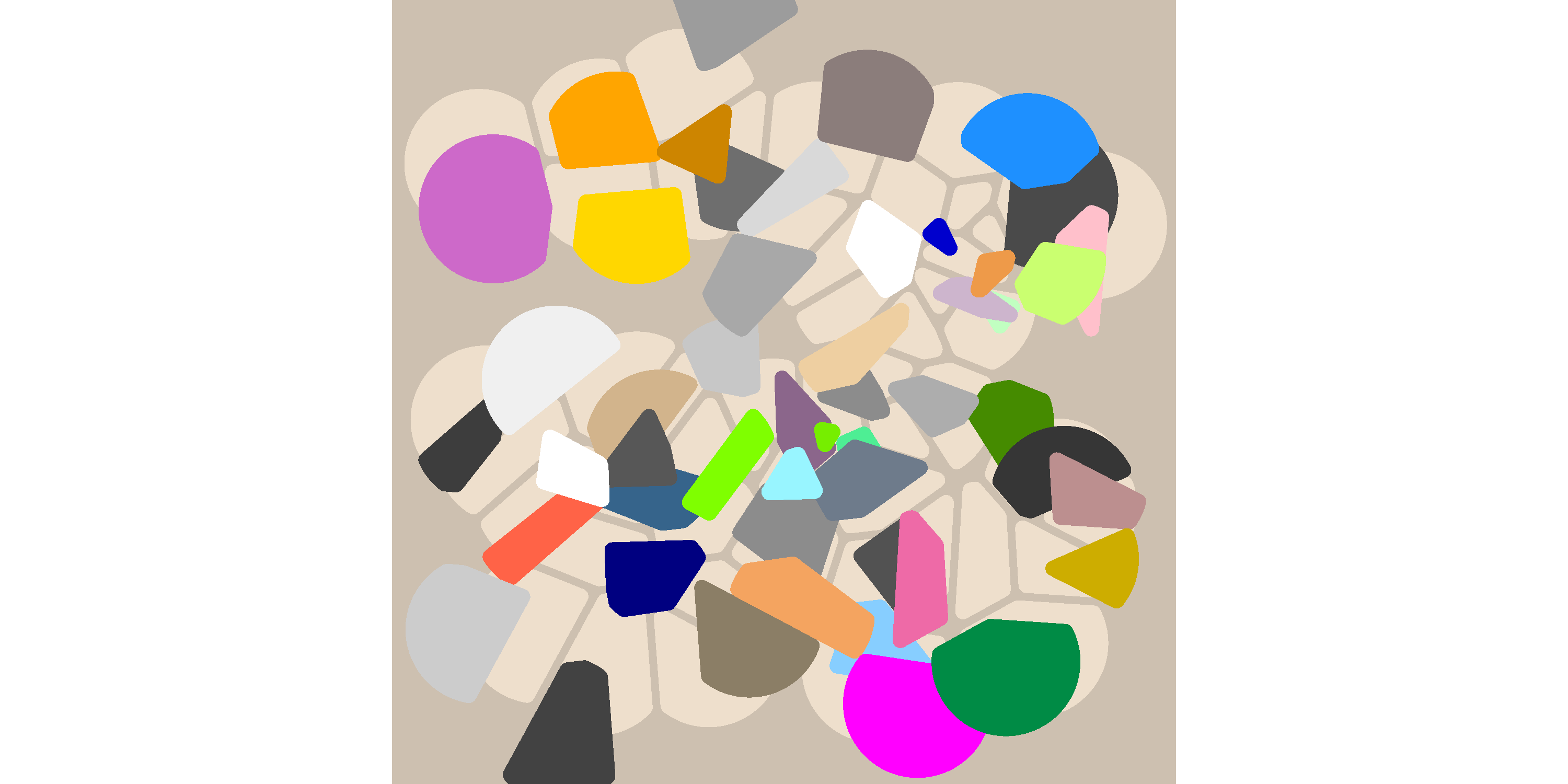
Note that perturb_uniform() returns a function. The voronoise package comes with a couple of handy functions that will create custom perturbing functions. For example:
voronoise_base(dat) + geom_voronoise(fill = "antiquewhite2") + geom_voronoise(perturb = perturb_float(-90))
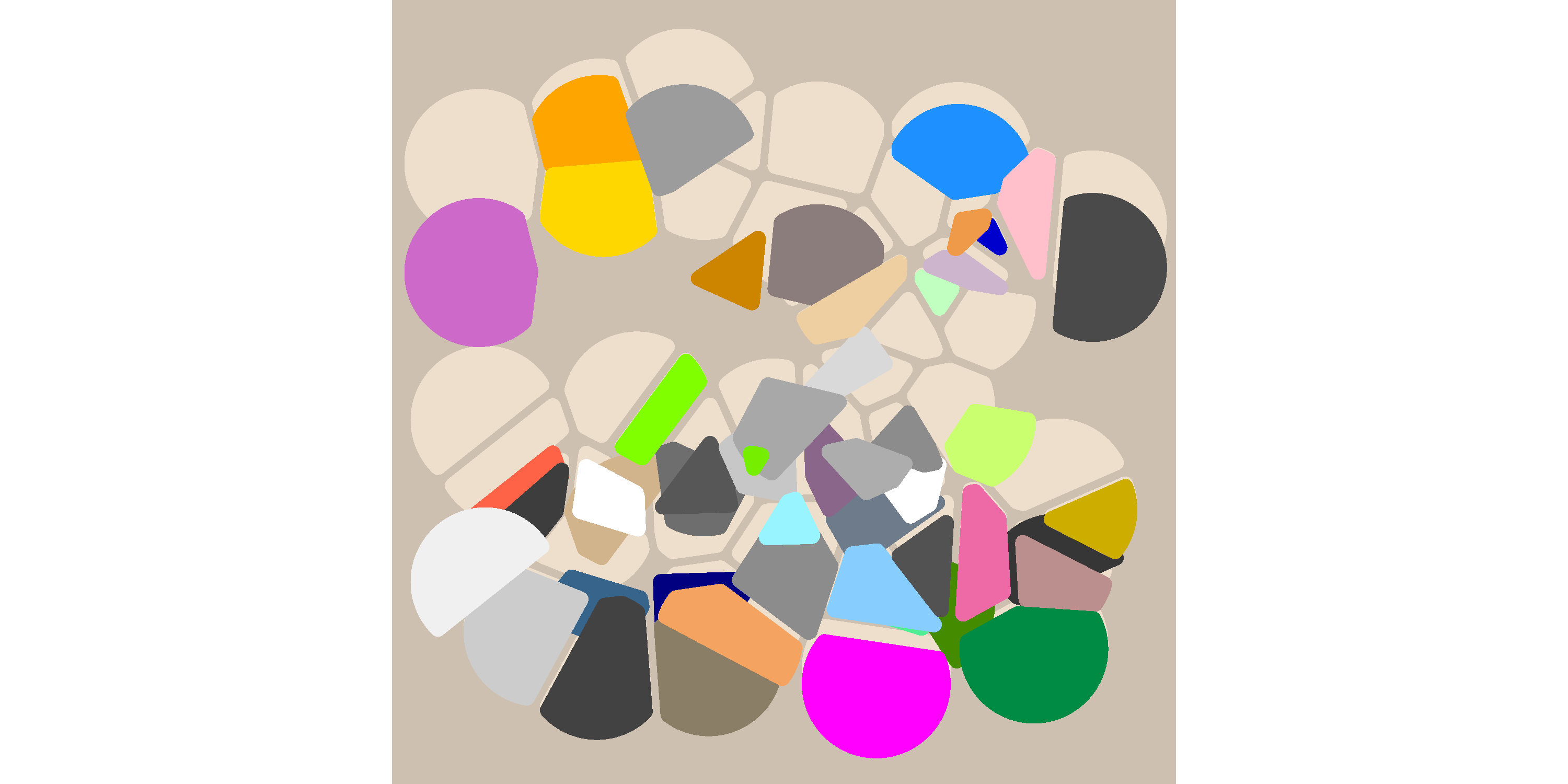
An example using some more settings:
set.seed(1) voronoise_base( data = voronoise_data(100, viridis::magma(10)), background = "skyblue3" ) + geom_voronoise(fill = "skyblue2") + geom_voronoise( perturb = perturb_float( angles = c(0, 90, 180), noise = c(2, 1) ) )